The journey of a fashion good from idea to finished product follows a varied but structured process. Each stage plays a critical role in ensuring that the product not only meets creative and aesthetic goals but also satisfies market demands and operational constraints.
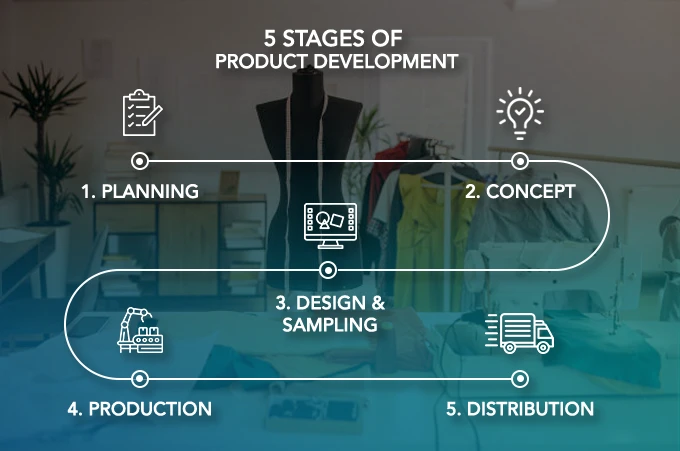
Below are the five key stages of fashion product development, each of which contributes to the successful launch of a fashion item.
1. Planning
The planning stage is where fashion brands lay the foundation for a successful product. Market research and trend analysis help identify the styles and preferences that are likely to resonate with consumers. This research informs the product’s overall direction and ensures that it meets market demand.
During planning, brands also address budgeting and resource allocation, determining the financial scope of the project and assigning resources across teams. Additionally, this phase involves creating an initial product roadmap, which outlines timelines, key milestones, and responsibilities for each department.
2. Concept
In the concept stage, the focus shifts to creativity. Designers begin creating mood boards, storyboards, and initial sketches to establish the visual direction of the product or collection. This is a collaborative phase, where designers work with merchandisers, product managers, and trend forecasters to ensure that the product vision aligns with both creative goals and market realities.
Once the concept is solidified, brands may engage with external partners like vendors and factories to discuss initial ideas, timelines, pricing and material availability. This early collaboration ensures that the product can be manufactured efficiently, and potential production issues are flagged early in the process.
3. Design & Sampling
The design stage is where the product starts to take a tangible form. Designers create detailed sketches, patterns, and prototypes. These prototypes, also called samples, allow teams to test the product’s fit, fabric, color and overall design adherence.
Each brand may do multiple types and rounds of sample revisions as they fine-tune details and adjust based on feedback from internal teams and external partners. Brands typically work closely with factories during this process to ensure that the samples meet both quality and production standards.
A tech pack, comprehensive technical specification document, is crucial at this stage. It includes all measurements, fabric details, and construction guidelines and serves as a blueprint for the manufacturer, ensuring that the product is produced according to the designer’s vision.
The Bill of Materials (BOM) is also developed at this stage which lists all materials, components, and trims needed to produce the product, along with their costs and suppliers. The BOM helps ensure that all necessary materials are available for production.
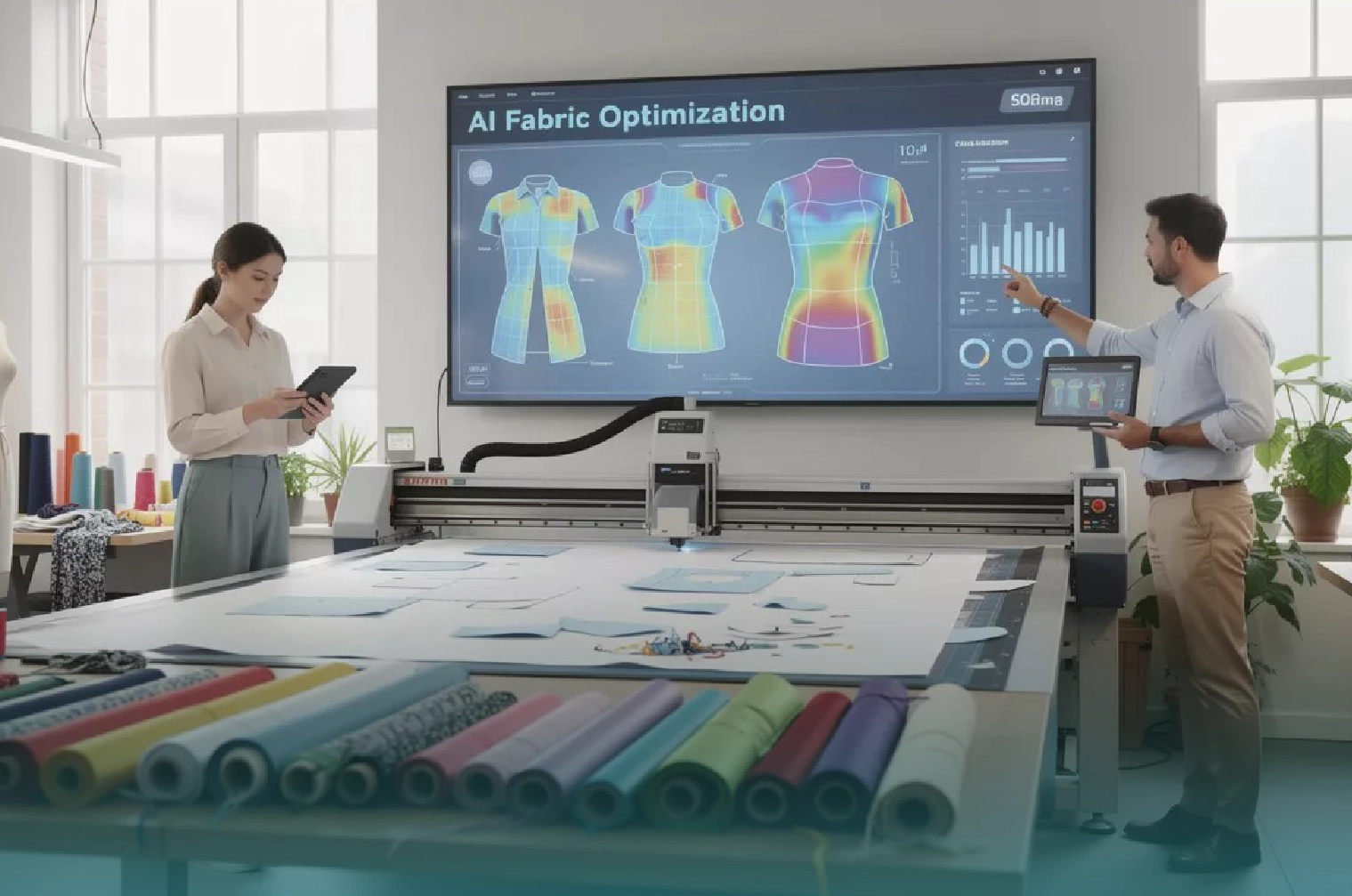
4. Production
Once samples are approved and the tech pack is finalized, the product moves into the production stage. This involves sourcing the necessary materials, selecting manufacturing partners, and setting a production timeline. Brands must collaborate closely with their vendors and factories to ensure that production runs smoothly, meets quality standards, and stays on schedule.
Quality control checks are critical during this stage. Regular inspections are carried out throughout the production process to catch any issues early and ensure that the final product aligns with the brand’s standards. Additionally, brands may order pre-production samples to verify that everything from materials to fit meets their expectations before mass production begins.
5. Distribution
In the final stage of product development, the finished products are prepared for distribution. This requires logistics planning, including arranging transportation and shipping products to retailers or directly to customers in the case of direct-to-consumer brands. Efficient logistics ensure that products reach the market on time and in good condition.
Brands also need to focus on inventory management and sales forecasting. Accurate demand forecasting helps prevent overproduction or underproduction, both of which can impact profitability. By monitoring inventory levels and adjusting production plans as needed, fashion brands can optimize their product flow and meet customer demand efficiently.